Understanding the Kinds Of Foreign Presents: Just How to Efficiently Report Them
Understanding international gifts is essential for organizations traversing complex reporting demands (report a foreign gift). These gifts can differ significantly, dropping into non-monetary and monetary classifications. Each kind offers one-of-a-kind challenges in appraisal and conformity. Organizations must know the legal and honest ramifications entailed. Efficient administration and reporting demand clear guidelines and normal training. The inquiry continues to be: how can companies assure they satisfy these obligations while keeping openness and liability?
Meaning and Review of Foreign Presents
Foreign gifts are things or advantages obtained from international entities, which can consist of people, governments, or organizations. These presents might take numerous forms, including concrete items, services, or other types of help that hold value. The significance of international gifts frequently exists in their possible to influence partnerships in between people, companies, or nations. They can be a way of diplomacy, showing a good reputation or cultivating collaboration. Nevertheless, the approval of such presents raises ethical and lawful considerations, specifically regarding openness and prospective problems of rate of interest. Receivers have to navigate complex regulations that control the coverage and acceptance of international presents, making sure compliance with both international and residential legislations. Understanding the interpretation and implications of international gifts is crucial for organizations and individuals to keep honesty and accountability in their transactions with international entities. This foundational expertise sets the stage for a deeper expedition of the different kinds of foreign gifts and their coverage demands.
Types of International Presents: Monetary vs. Non-Monetary
Presents from abroad can be classified right into 2 major kinds: monetary and non-monetary. Monetary gifts encompass direct monetary payments, such as money or checks, which can substantially influence the recipient's economic standing. These gifts are typically straightforward to value and record, as they involve clear financial quantities.
Non-monetary gifts, on the other hand, consist of concrete things such as garments, artwork, or mementos, in addition to abstract offerings like solutions or experiences. While these presents might not have a straight economic impact, they can hold considerable sentimental or social worth. Valuing non-monetary presents can be more intricate, as it usually requires examining the item's market worth or value to the recipient. Recognizing these two groups is essential for accurate reporting, making certain conformity with regulations keeping and regarding foreign gifts transparency in monetary negotiations.
Honest and lawful Ramifications of Receiving Foreign Present
While the attraction of getting gifts from abroad might appear harmless, the honest and lawful ramifications related to such deals can be considerable. Receivers need to browse complex policies that govern the acceptance of foreign gifts, as failure to do so may cause lawful repercussions, including permissions or fines. Fairly, the approval of gifts from international entities can lead to understandings of favoritism or problems of interest, particularly for people ready of power or public depend on. Such understandings can weaken the integrity of institutions and deteriorate public confidence. In addition, the capacity for foreign impact elevates worries relating to national safety and security and the integrity of decision-making procedures. Consequently, individuals should carefully take into consideration not just the validity of accepting international gifts but additionally the wider implications on their credibilities and the institutions they stand for. Ultimately, thoughtful consideration is vital to preserve both lawful compliance and ethical criteria.
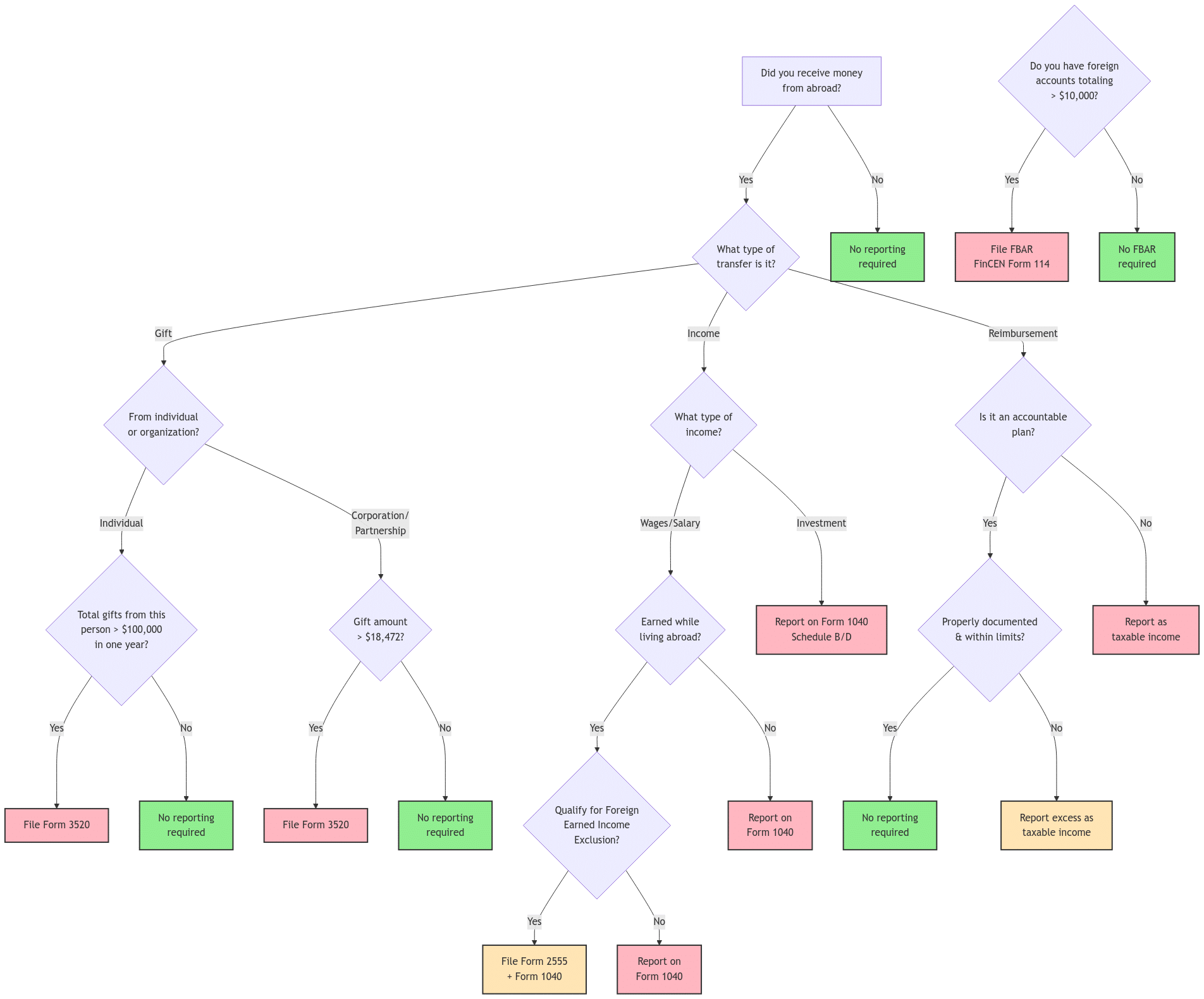
Reporting Demands for Foreign Presents

Recognizing the reporting needs related to receiving international presents is essential for individuals in numerous industries, particularly those in government and civil service. These requirements are created to advertise openness and protect against conflicts of rate of interest. Typically, receivers should report any type of international presents exceeding a specified monetary threshold, which varies by jurisdiction.
Documentation is vital, as receivers must offer information such as the worth, nature, and resource of the gift, in addition to the day it was gotten. Many organizations need receivers to send their records within an assigned timeframe, usually within 30 days of receipt.

Failure to conform with these reporting responsibilities can bring about extreme effects, consisting of lawful fines and damages to one's specialist reputation. Therefore, understanding the particular regulations suitable to one's placement and territory is necessary for making certain conformity and keeping honest requirements in civil service.
Ideal Practices for Taking Care Of Foreign Gifts in Organizations
To effectively manage international gifts within organizations, establishing clear plans and procedures is essential. Organizations should begin by specifying what makes up an international gift and recognizing the relevant coverage requirements to assure conformity with legal commitments. Routine training sessions can check my source enhance staff recognition of these policies, advertising a culture of transparency and persistance.
Additionally, companies need to apply a centralized monitoring system to document all foreign presents obtained, including details such as the resource, value, and purpose. report a foreign gift. This system ought to facilitate routine testimonials and audits to examine compliance with established policies

Regularly Asked Inquiries
Can Foreign Present Influence Business Choices or Relationships?
Foreign gifts can notably affect company choices and partnerships, usually producing perceived responsibilities or predispositions. Such influences might affect arrangements, collaborations, and overall company principles, potentially leading to problems of interest or reputational threats.
What Are the Penalties for Failing to Report Foreign Present?
Stopping working to report international gifts can cause significant fines, including penalties, disciplinary activity, or lawful repercussions. Noncompliance threatens transparency and might damage reputations, highlighting the importance of adhering to reporting policies.
Are There Specific Countries With Stricter Present Regulations?
Certain countries, like China and Saudi Arabia, apply stricter guidelines on gifts, showing social norms and governmental oversight. These guidelines might influence international communications and necessitate careful factor to consider by people engaging in cross-border relationships.
Just How Can Organizations Educate Employees Regarding Foreign Present Policies?
Organizations can enlighten employees regarding international present policies through normal training sessions, complete handbooks, and clear interaction home networks. Involving workshops and real-life scenarios assist enhance understanding, making certain compliance and awareness of prospective moral predicaments.
What Documentation Is Required for International Present Coverage?
Documentation for foreign gift reporting typically includes a comprehensive description of the present, its worth, the benefactor's details, objective of the gift, and any appropriate policies or regulations regulating the approval and reporting of such gifts.
Foreign gifts are advantages or products obtained from international entities, which can include companies, governments, or individuals. Recipients have to browse complicated guidelines that govern the reporting and approval of international gifts, making sure conformity with both domestic and international regulations. Recognizing the meaning and ramifications of foreign gifts is necessary for organizations and people to keep stability and accountability in their dealings with international entities. Receivers should browse intricate laws that regulate the acceptance of international gifts, as failure to do so might result in other lawful effects, including fines or assents. Stopping working to report international presents can result in considerable fines, including fines, corrective activity, or legal effects.